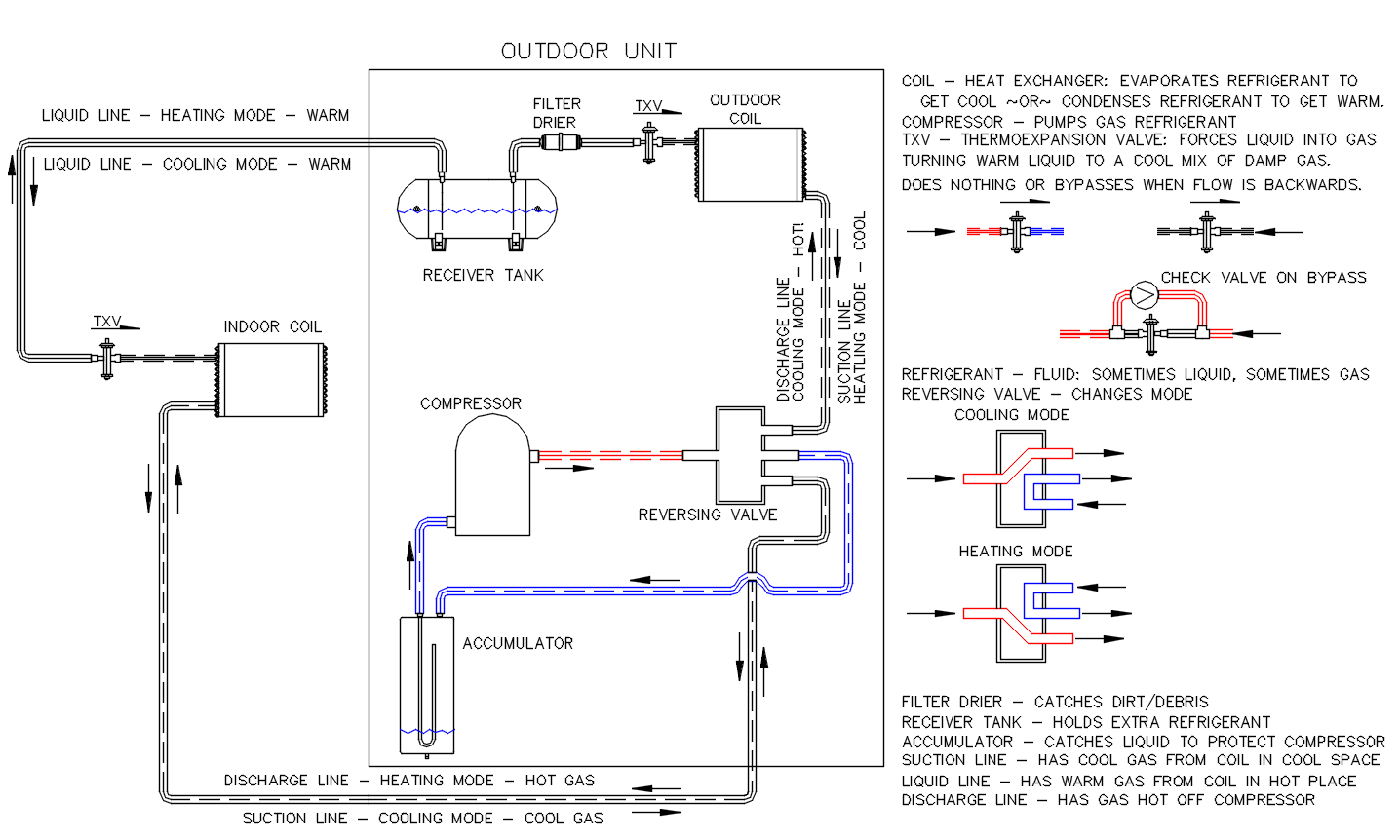
A heat pump is a type of HVAC equipment that transfers heat between two mediums via a direct expansion refrigeration cycle to provide heating or cooling based on the demands of the space.
A heat pump functions the same way as a traditional HVAC system when cooling down a space.A traditional HVAC cooling system consists of:
- Expansion Valve – reduces the refrigerant pressure
- Evaporator (Coil) – a heat exchanger allows the refrigerant to absorb heat
- Compressor – compresses the refrigerant to increase its pressure
- Condenser – a heat exchanger that rejects the heat from the refrigerant to the outside. This allows the hot refrigerant off the compressor to cool and cycle back indoors to absorb more heat.

These components are connected via refrigerant piping creating a loop through which the refrigerant circulates. During cooling operation, the refrigerant continues to circulate within this closed loop system extracting heat from the space and rejecting it to the exterior of the building.
What makes the heat pump different than a traditional HVAC system is its ability to use this same DX cycle to also provide heating.
A heat pump accomplishes this by switching the roles of the evaporator and condenser in the cycle, by changing the direction of the refrigerant flow using a component called a reversing valve.

A more detailed layout for a heat pump system with some very basic definitions is below.